Page 6 - SAC-Gender-Responsive-Market-Analysis-Final-Report-July-19-2021 (1)
P. 6
2. Regional root cause analysis
The root causes of inequity
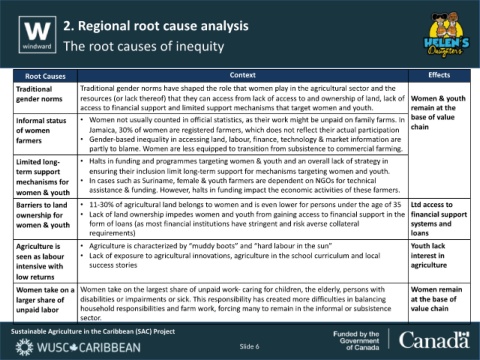
Root Causes Context Effects
Traditional Traditional gender norms have shaped the role that women play in the agricultural sector and the
gender norms resources (or lack thereof) that they can access from lack of access to and ownership of land, lack of Women & youth
access to financial support and limited support mechanisms that target women and youth. remain at the
Informal status • Women not usually counted in official statistics, as their work might be unpaid on family farms. In base of value
of women Jamaica, 30% of women are registered farmers, which does not reflect their actual participation chain
farmers • Gender-based inequality in accessing land, labour, finance, technology & market information are
partly to blame. Women are less equipped to transition from subsistence to commercial farming.
Limited long- • Halts in funding and programmes targeting women & youth and an overall lack of strategy in
term support ensuring their inclusion limit long-term support for mechanisms targeting women and youth.
mechanisms for • In cases such as Suriname, female & youth farmers are dependent on NGOs for technical
women & youth assistance & funding. However, halts in funding impact the economic activities of these farmers.
Barriers to land • 11-30% of agricultural land belongs to women and is even lower for persons under the age of 35 Ltd access to
ownership for • Lack of land ownership impedes women and youth from gaining access to financial support in the financial support
women & youth form of loans (as most financial institutions have stringent and risk averse collateral systems and
requirements) loans
Agriculture is • Agriculture is characterized by “muddy boots” and “hard labour in the sun” Youth lack
seen as labour • Lack of exposure to agricultural innovations, agriculture in the school curriculum and local interest in
intensive with success stories agriculture
low returns
Women take on a Women take on the largest share of unpaid work- caring for children, the elderly, persons with Women remain
larger share of disabilities or impairments or sick. This responsibility has created more difficulties in balancing at the base of
unpaid labor household responsibilities and farm work, forcing many to remain in the informal or subsistence value chain
sector.
Sustainable Agriculture in the Caribbean (SAC) Project
Slide 6