Page 64 - SAC-Gender-Responsive-Market-Analysis-Final-Report-July-19-2021 (1)
P. 64
2. Root cause analysis
Understanding root causes and effects in detail
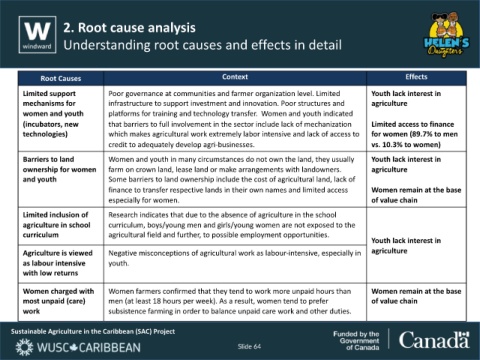
Root Causes Context Effects
Limited support Poor governance at communities and farmer organization level. Limited Youth lack interest in
mechanisms for infrastructure to support investment and innovation. Poor structures and agriculture
women and youth platforms for training and technology transfer. Women and youth indicated
(incubators, new that barriers to full involvement in the sector include lack of mechanization Limited access to finance
technologies) which makes agricultural work extremely labor intensive and lack of access to for women (89.7% to men
credit to adequately develop agri-businesses. vs. 10.3% to women)
Barriers to land Women and youth in many circumstances do not own the land, they usually Youth lack interest in
ownership for women farm on crown land, lease land or make arrangements with landowners. agriculture
and youth Some barriers to land ownership include the cost of agricultural land, lack of
finance to transfer respective lands in their own names and limited access Women remain at the base
especially for women. of value chain
Limited inclusion of Research indicates that due to the absence of agriculture in the school
agriculture in school curriculum, boys/young men and girls/young women are not exposed to the
curriculum agricultural field and further, to possible employment opportunities.
Youth lack interest in
Agriculture is viewed Negative misconceptions of agricultural work as labour-intensive, especially in agriculture
as labour intensive youth.
with low returns
Women charged with Women farmers confirmed that they tend to work more unpaid hours than Women remain at the base
most unpaid (care) men (at least 18 hours per week). As a result, women tend to prefer of value chain
work subsistence farming in order to balance unpaid care work and other duties.
Sustainable Agriculture in the Caribbean (SAC) Project
Slide 64