Page 51 - SAC-Gender-Responsive-Market-Analysis-Final-Report-July-19-2021 (1)
P. 51
2. Root cause analysis
Understanding root causes in more detail
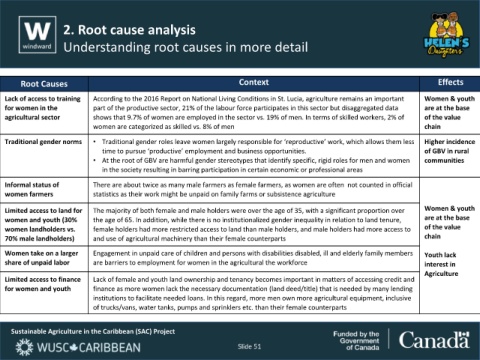
Root Causes Context Effects
Lack of access to training According to the 2016 Report on National Living Conditions in St. Lucia, agriculture remains an important Women & youth
for women in the part of the productive sector, 21% of the labour force participates in this sector but disaggregated data are at the base
agricultural sector shows that 9.7% of women are employed in the sector vs. 19% of men. In terms of skilled workers, 2% of of the value
women are categorized as skilled vs. 8% of men chain
Traditional gender norms • Traditional gender roles leave women largely responsible for ‘reproductive’ work, which allows them less Higher incidence
time to pursue ‘productive’ employment and business opportunities. of GBV in rural
• At the root of GBV are harmful gender stereotypes that identify specific, rigid roles for men and women communities
in the society resulting in barring participation in certain economic or professional areas
Informal status of There are about twice as many male farmers as female farmers, as women are often not counted in official
women farmers statistics as their work might be unpaid on family farms or subsistence agriculture
Limited access to land for The majority of both female and male holders were over the age of 35, with a significant proportion over Women & youth
women and youth (30% the age of 65. In addition, while there is no institutionalized gender inequality in relation to land tenure, are at the base
women landholders vs. female holders had more restricted access to land than male holders, and male holders had more access to of the value
70% male landholders) and use of agricultural machinery than their female counterparts chain
Women take on a larger Engagement in unpaid care of children and persons with disabilities disabled, ill and elderly family members Youth lack
share of unpaid labor are barriers to employment for women in the agricultural the workforce interest in
Agriculture
Limited access to finance Lack of female and youth land ownership and tenancy becomes important in matters of accessing credit and
for women and youth finance as more women lack the necessary documentation (land deed/title) that is needed by many lending
institutions to facilitate needed loans. In this regard, more men own more agricultural equipment, inclusive
of trucks/vans, water tanks, pumps and sprinklers etc. than their female counterparts
Sustainable Agriculture in the Caribbean (SAC) Project
Slide 51