Page 92 - SAC-Gender-Responsive-Market-Analysis-Final-Report-July-19-2021 (1)
P. 92
2. Root cause analysis
Understanding root causes & effects in detail
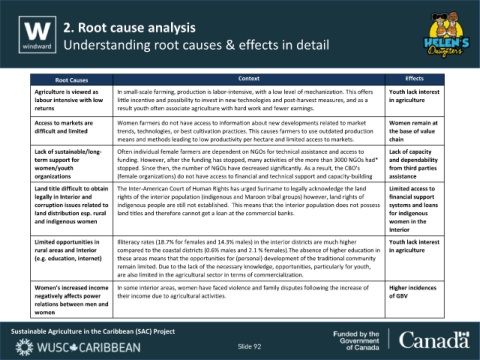
Root Causes Context Effects
Agriculture is viewed as In small-scale farming, production is labor-intensive, with a low level of mechanization. This offers Youth lack interest
labour intensive with low little incentive and possibility to invest in new technologies and post-harvest measures, and as a in agriculture
returns result youth often associate agriculture with hard work and fewer earnings.
Access to markets are Women farmers do not have access to information about new developments related to market Women remain at
difficult and limited trends, technologies, or best cultivation practices. This causes farmers to use outdated production the base of value
means and methods leading to low productivity per hectare and limited access to markets. chain
Lack of sustainable/long- Often individual female farmers are dependent on NGOs for technical assistance and access to Lack of capacity
term support for funding. However, after the funding has stopped, many activities of the more than 3000 NGOs had* and dependability
women/youth stopped. Since then, the number of NGOs have decreased significantly. As a result, the CBO's from third parties
organizations (female organizations) do not have access to financial and technical support and capacity-building assistance
Land title difficult to obtain The Inter-American Court of Human Rights has urged Suriname to legally acknowledge the land Limited access to
legally in Interior and rights of the interior population (indigenous and Maroon tribal groups) however, land rights of financial support
corruption issues related to indigenous people are still not established. This means that the interior population does not possess systems and loans
land distribution esp. rural land titles and therefore cannot get a loan at the commercial banks. for indigenous
and indigenous women women in the
Interior
Limited opportunities in Illiteracy rates (18.7% for females and 14.3% males) in the interior districts are much higher Youth lack interest
rural areas and Interior compared to the coastal districts (0.6% males and 2.1 % females).The absence of higher education in in agriculture
(e.g. education, internet) these areas means that the opportunities for (personal) development of the traditional community
remain limited. Due to the lack of the necessary knowledge, opportunities, particularly for youth,
are also limited in the agricultural sector in terms of commercialization.
Women’s increased income In some interior areas, women have faced violence and family disputes following the increase of Higher incidences
negatively affects power their income due to agricultural activities. of GBV
relations between men and
women
Sustainable Agriculture in the Caribbean (SAC) Project
Slide 92